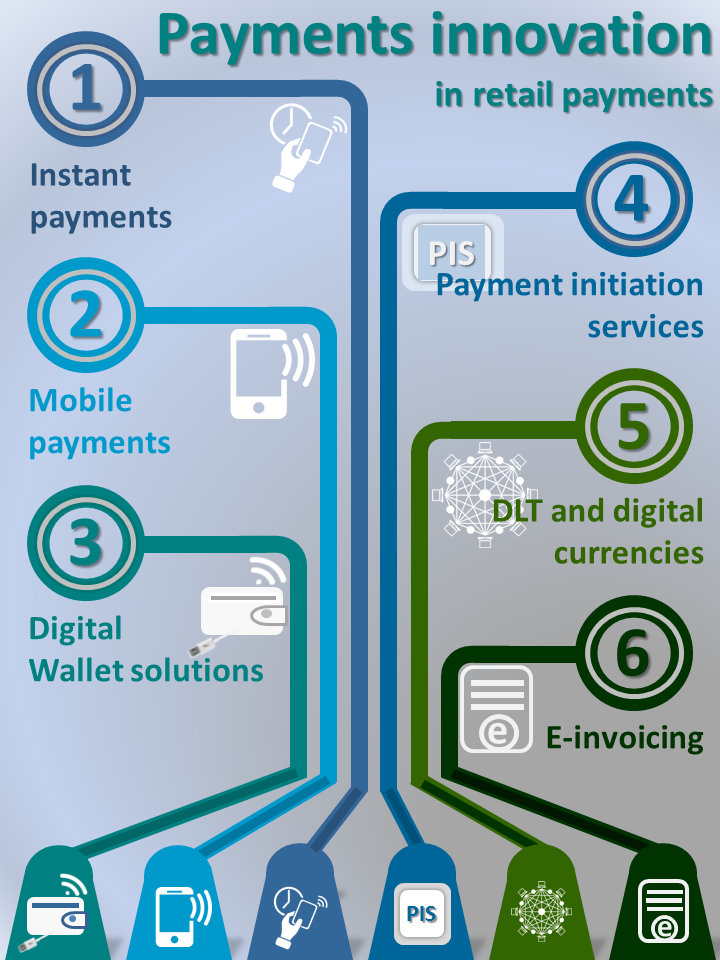
In recent years, the euro retail payments market is developing and offers innovative payment solutions.
This is expected to further accelerate in the coming years, due to the technological, social and economic changes associated with digitalisation , and due to the fact that the EU regulatory framework allows non-standard service providers to enter the retail payment market.
Furthermore, retail payments innovation and financial technology (FinTech) also have an impact on the operation of payment systems. Committed to promoting the smooth and efficient operation of payment systems, the European Central Bank (ECB) and national central banks (NCBs) constantly study and analyse developments in payments, in order to help create and maintain a harmonised regulatory framework that prevents market fragmentation and ensures a level playing field across Europe for both end users and service providers.
Against this background, innovative payment solutions are key to delivering a single and competitive market for retail payments in euro. In order for these solutions not to act as barriers to market entry or give rise to fragmentation in payment services offered across Europe, or even threaten the safety and integrity of payment systems, the Bank of Greece, as one of the Eurosystem NCBs, carries out research and analysis with a primary focus on the following areas: